|
|
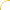 |
difference mode
|  |
 Description:
Description:
Both parameters are subtracted from one another, the absolute value is taken.
So the result shows the distance between both parameters, black stands for equal colors,
white for opposite colors (one is black, the other white).
The result looks a bit strange in many cases.
This mode can be used to invert parts of the base image,
and to compare two images (results in black if they are equal).
An interesting note: Unlike XOR mode, this mode (generally) cannot be undone by applying it twice,
but applying it three times, you get the same result as applying it once (and so on).
Formula:
f(a,b) = |a - b|

Advantage:
This mode is commutative (base and blend color can be swapped).
Code:
|
|
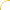 |
negation mode
|  |
 Description:
Description:
This one is the "opposite" of difference mode.
Note that it is NOT difference mode inverted, because black and white return the same result,
but colors between become brighter instead of darker.
This mode can be used to invert parts of the base image,
but NOT to compare two images.
An interesting note: Unlike XOR mode, this mode (generally) cannot be undone by applying it twice,
but applying it three times, you get the same result as applying it once (and so on).
Since I didn't see this "forgotten" mode somewhere else, I gave it this (not that perfect) name.
Formula:
f(a,b) = 1 - |1 - a - b|

Advantage:
This mode is commutative (base and blend color can be swapped).
Code:
|
|
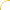 |
exclusion mode
|  |
 Description:
Description:
This mode is between difference and negation mode.
Again black and white return the same result,
but colors between become gray.
This mode can be used to invert parts of the base image,
but NOT to compare two images.
Formula:
f(a,b) = a + b - 2ab
or
f(a,b) = average(difference(a,b),negation(a,b))

Advantage:
This mode is commutative (base and blend color can be swapped).
Code:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

