|
|
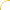 |
additive mode
|  |
 Description:
Description:
A very basic blend mode.
Formula:
f(a,b) = a + b

Advantage:
This mode is commutative (base and blend color can be swapped).
Disadvantage:
The formula can result in values greater than 1, so some truncation can occur.
Code:
|
|
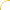 |
subtractive mode
|  |
 Description:
Description:
The "opposite" of additive mode.
In fact the same as additive mode, but darker - dark colors are truncated instead of bright colors
(the "real opposite" would be a - b, what can be done by inverting the blend image).
Formula:
f(a,b) = a + b - 1

Advantage:
This mode is commutative (base and blend color can be swapped).
Disadvantage:
The formula can result in values smaller than 0, so some truncation can occur.
Code:
|
|
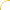 |
stamp mode
|  |
 Description:
Description:
This mode somehow is similar to average mode.
It is helpful when applying relief or bump textures to images (that's why I gave it this name).
Gray blend colors do not change the background,
brighter or darker colors make the background brighter or darker.
The result can become very extreme, so this mode works best with medium colors.
Formula:
f(a,b) = a + 2b - 1
Disadvantage:
The formula can result in values smaller than 0 or greater than 1, so some truncation can occur.
Code:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

